As today’s globally competitive landscape requires companies to tailor their organizations to be more responsive to local and regional market and customer requirements, they also must deal with increasing challenges for enterprise-wide integration and efficiency.
Many companies are dealing with these issues by implementing Shared Service Organizations (SSOs) and Financial Shared Services Centers (FSSCs). Basically, these shared services approaches enable consolidation of certain business operations that are then available to multiple business entities across the enterprise.
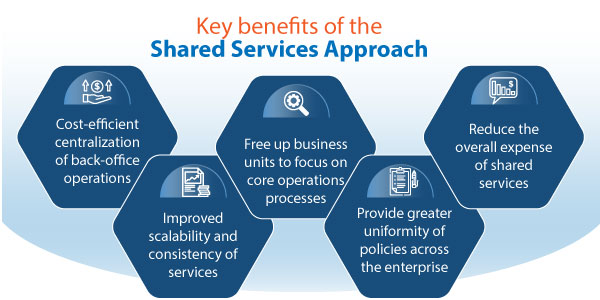
Key benefits of the shared services approach include:
- Cost-efficient centralization of back-office operations.
- Improved scalability and consistency of services.
- Free up business units to focus on core operations processes.
- Provide greater uniformity of policies across the enterprise.
- Reduce the overall expense of shared services.
Historically, the shared service concept goes back decades with the advent of “typing pools” in the 1920s to reduce the cost of buying typewriters and hiring skilled typists in every department. Today, most companies have some form of shared services, most often providing centralized HR and IT functions that span the whole company.
In recent years, the shared services and centralized applications approach has been increasingly used for financial processes, including AR/AP, revenue recognition, compliance, order-to-cash (OTC), procure-to-pay, payment factory, asset management, multi-bank connectivity (MBC), in-house cash, and many others.
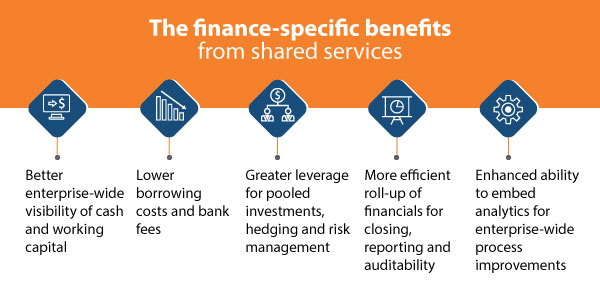
Some of the finance-specific benefits from shared services include:
- Better enterprise-wide visibility of cash and working capital.
- Lower borrowing costs and bank fees.
- Greater leverage for pooled investments, hedging and risk management.
- More efficient roll-up of financials for closing, reporting and auditability.
- Enhanced ability to embed analytics for enterprise-wide process improvements.
Of course, when it comes to implementing shared services, there are challenges as well as benefits.
It is critical to create a shared service model that balances the goals of centralization with the need to conform with the variety of disparate local regulations on things like taxes, reporting, privacy laws, business practices, etc.
At the same time, it is imperative that the shared services processes include tightly integrated security functionality to assure stringent data integrity, access controls, user identity management, fraud prevention, and compliance mechanisms.
As SAP’s longest serving partner with a nearly 25-year track record, Bramasol continues to innovate in the deployment of shared services in the finance arena, along with a constant focus on assuring tightly integrated security capabilities.
Some of the specific advantages of SAP’s shared service tools and security ecosystem include the following.
 SAP Data Retention Manager – provides system-wide data retention, residence, and security rules to protect transactional and personal data across various SAP applications, along with the ability to tailor policies for specific regional privacy and regulatory requirements, such as GDPR.
SAP Data Retention Manager – provides system-wide data retention, residence, and security rules to protect transactional and personal data across various SAP applications, along with the ability to tailor policies for specific regional privacy and regulatory requirements, such as GDPR.
 SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance – streamlines identity and access management (IAM) across both cloud and on-premise environments to provide centralized, configurable, dashboard-driven control of access policies.
SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance – streamlines identity and access management (IAM) across both cloud and on-premise environments to provide centralized, configurable, dashboard-driven control of access policies.
 SAP Single Sign-On – simplifies user access management for both SAP and non-SAP applications with integrated cybersecurity protocols and streamlined administration.
SAP Single Sign-On – simplifies user access management for both SAP and non-SAP applications with integrated cybersecurity protocols and streamlined administration.
 SAP Access Control – manages and validates user access with governance software that automates user provisioning and certification for applications and data.
SAP Access Control – manages and validates user access with governance software that automates user provisioning and certification for applications and data.
 SAP Security Optimization – decreases the risk of system intrusion, ensures authenticity of users, assures confidentiality of business data, reduces risks of downtime and enables hyperscaling of systems.
SAP Security Optimization – decreases the risk of system intrusion, ensures authenticity of users, assures confidentiality of business data, reduces risks of downtime and enables hyperscaling of systems.
While each of these targeted security applications are important, an overarching advantage of the SAP ecosystem is the ability to build these security functions into virtually every application across the entire technology stack.
In addition, looking ahead to a smooth migration to S/4HANA’s performance and integration advantages gives companies an assurance that all their investments in shared services and security functions will continue to pay dividends over the long term.
More broadly, the comprehensive scope of the RISE with SAP initiative is providing a holistic view of digital transformation that encompasses the entire spectrum of customers, vendors, suppliers, partners, and in-house users, thereby laying a foundation for extending shared services to integrate the needs of external and internal stakeholders – while maintaining a secure and integrated environment.
Check out these resources to learn more:
- Podcast: SAP's Birgit Starmanns Discusses Centralization vs. Decentralization for Finance & Risk
- S/4HANA Readiness Assessment
- Overview of RISE with SAP initiative
- Video: Developing a Cost Effective, Secure, Scalable Banking Strategy with SAP MBC

